





Published on Nov 30, 2023
Polyfuse is a new standard for circuit protection. It is resettable. Many manufacturers also call it polyswitch or multifuse. Polyfuses are not fuses but polymeric positive temperature co-efficient (PPTC) thermistors.
Current limiting can be accomplished by using resistors , fuses , switches or positive temperature co-efficient devices. Resistors are rarely an acceptable solution because the high power resistors that are usually required are expensive. One-shot fuses can be used, but they might fatigue, and they must be replaced after a fault event. Ceramic PTC devices tends to have high resistance and power dissipation characteristics.
The preferred solution is a PPTC device which has low resistance in normal operation and high resistance when exposed to a fault. Electrical shorts or electrically over-loaded circuits can cause over-current and over temperature damage.
Like traditional fuses, PPTC devices limit the flow of dangerously high current during fault conditions. Unlike traditional fuses, PPTC devices reset after the fault is cleared and the power to the circuit is removed.
Technically, polyfuses are not fuses but polymeric positive temperature co-efficient (PPTC) thermistors. For thermistors characterized as positive temperature co-efficient, the device resistance increases with temperature. These comprise thin sheets of conductive plastic with electrodes attached to either side. The conductive plastic is basically a non-conductive crystalline polymer loaded with a highly conductive carbon to make it conductive. The electrodes ensure even distribution of power throughout the device.
Polyfuses are usually packaged in radial, axial, surface- mount, chip, disk or washer form, these are available in voltage ratings of 30 to 250 volts and current ratings of 20Ma to 100 amps.
PPTC circuit protection devices are formed from a composite of semi crystalline polymer and conductive particles. At normal temperatures, the conductive particles form low resistance networks in the polymer. However if temperature rises above the device's switching temperature, either from high current through the part or from an increase in the ambient temperature, the crystallites in the polymer melt and become amorphous. The increase in volume during melting of crystalline phase causes separation of conductive particles and results in a large non linear increase in resistance of the device.
The resistance typically increases by three or more orders of magnitude as shown in figure 1. The increased resistance protects the equipment in the circuit by reducing the amount of current that can flow under the fault condition to a low steady state level. The device will remain in its latched (high resistance) position until the fault is cleared and power to the circuit is removed at which time the conductive composite cools and recrystallises , restoring the PPTC to a low resistance state and the circuit and the circuit and the affected equipment to normal operating conditions.
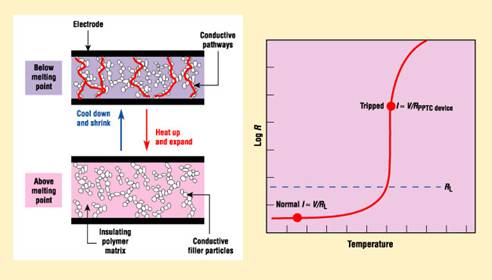
Thus a polyfuse acts like a self-resetting solid state circuit breaker, which makes it suitable for providing low-cost over-protection device. The resistance of polyfuse (expressed on log scale) at room temperature is a few ohms and rapidly increases above 110 degree Celsius.
PPTC devices protect the circuit by going from a low steady state to a high resistance state in response to an over-current or over temperature condition.
This surface mount polyfuse family of polymer of polymer based resettable fuses provides reliable overcurrent protection for a wide range of products such as computer motherboards, USB hubs and ports , CD/DVD drives , digital cameras and battery packs. Each of these polyfuse series features low voltage drops and fast trip times while offering full resettability. This makes each an ideal choice for protection in datacom and battery powered applications where momentary surges may occur during interchange of batteries or plug and play operations.
The SMD0805 with the industry’s smallest footprint, measuring only 2.2mm by 1.5mm, features four hold current ratings from 100mA to 500mA with a current interruption capability of 40A at rated voltage. Both the SMD1206 and SMD1210 series are optimized for protection of computer peripherals,PC cards and various port types.
Due to the automatic resetting of the polyfuse , these components are ideal for applications, where temporary fault conditions (eg: during hot plugging) can occur. The radial-leaded RLD-USB-series 709 is specifically designed for universal serial bus (USB) applications with lower resistance, faster trip times and lower voltage drops.
This type profile strap type polyfuse family of resettable fuses provides thermal and over charge protection for rechargeable battery packs commonly used in portable electronics such as mobile phones, notebook computers and camcorders.
Both Li-Ion and NiMH pack designs are enhanced with 0.8mm high form factor on the VTD-719 series. The LTD-717 series is optimized for prismatic packs and exhibits faster trip times- down to 2.9 sec at five times the fuse’s hold current rating
| Are you interested in this topic.Then mail to us immediately to get the full report.
email :- contactv2@gmail.com |